STP (Sewage Treatment Plant)
Sewage Treatment Plant or simply STP is a highly demanded product amongst others in Allied Enviro company. The company is providing repairs and maintenance services in all over India at an affordable price and through the expert and efficient engineers. Sewage treatment is performed to clean the waste water underlying in land. This waste water is the result of domestic and commercial disposals, rain water etc. Thus, sewage treatment is performed to remove the majority of the contaminants lying in waste water and to produce the smooth flow of liquid which should be environment friendly. Apart from this, it helps in keeping the environment clean.
Technologies used in Sewage Treatment System
MBBR (MOVING BED BIOFILM REACTOR)
MBBR technology employs thousands of polyethylene biofilm carriers operating in mixed motion within an aerated wastewater treatment basin. Each individual biocarrier increases productivity through providing protected surface area to support the growth of heterotrophic and autotrophic bacteria within its cells. It is this high-density population of bacteria that achieves high-rate biodegradation within the system, while also offering process reliability and ease of operation. This technology provides cost-effective treatment with minimal maintenance since MBBR processes self-maintain an optimum level of productive biofilm. Additionally, the biofilm attached to the mobile biocarriers within the system automatically responds to load fluctuations.
MBR (MEMBRANE BIO-REACTOR)
The term 'membrane bioreactor' (MBR) is generally used to define wastewater treatment processes where a perm-selective membrane like microfiltration or ultrafiltration is integrated with a biological process – a suspended growth bioreactor. Membrane bioreactor (MBR) technology has emerged as a wastewater treatment technology of choice over the activated sludge process (ASP), which has been the conventional municipal wastewater technology over the last century. MBR is, in fact, one of the most important innovations in wastewater treatment, as it overcomes the drawbacks of the conventional ASP, including large space requirement for secondary clarifiers, liquid–solid separation issues, production of excess sludge, and limitations with removal of recalcitrant. MBRs have been used for both municipal and industrial wastewater treatment and reclamation. An MBR is a hybrid of a conventional biological treatment system and physical liquid–solid separation system using membrane filtration in one system.
SBR (SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR)
Sequencing batch reactors or SBRs use a separate pre-treatment section to mechanicallyholdbacksolidsanda biological aeration and settling tank. Small SBR wastewater treatment systems clean incoming wastewater over a number of cycles. The wastewater goes first into primary treatment (1st chamber), where the solid substances are retained. From there, the wastewater is fed into the SBR tank (2nd chamber). The actual biological cleaning by microorganisms now takes place in the SBR tank. Short aeration and rest phases alternate in a controlled cleaning process. The so-called activated sludge can now develop with millions of microorganisms and clean the water thoroughly. A rest phase now follows, during which the live sludge sinks to the bottom of the system. This allows a clarified water zone to form at the top of the SBR tank. The purified wastewater is now fed into a discharge system (stream, river, lake) or into an infiltration system. Afterwards, the sludge is fed back from the SBR tank into the first.
SAF (SUBMERGED AERATED FILTER)
The SAF is an up-flow bioreactor which employs a high efficiency neutral buoyancy plastic media. The SAF consists of a containment vessel made in either GRP, GCS, coated mild steel, stainless steel or concrete with internal dividing walls, internal air and water distribution systems, charge of plastic media and internal support structure. The media provides a large surface area on which the bacteria attach themselves to grow and live. Wastewater is introduced into the base of the SAF unit. Air is introduced into the SAF through a separate diffuser system also located near the base of the unit. An air blower supplies oxygen to the SAF environment on a continuous basis. The air and water distribution system design is such that it creates a very effective mixing pattern within the SAF. This pattern allows for rapid distribution of the wastewater throughout the packed media bed. This produces a homogeneous solution in full contact with the entire microbial population for the period of time that the wastewater is in the reactor.
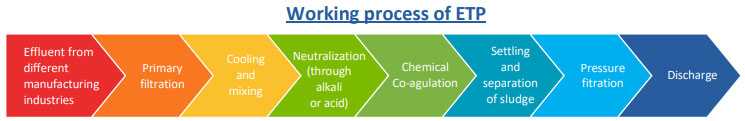
Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
Nowadays effluent has gained a wider coverage as it includes almost every waste that pour into our water and air. Liquid factory waste, smoke, and raw sewage can all be called effluents. Effluent Treatment Plants are another form of waste water treatment plants which are designed and manufactured specially for treating water that contains effluents and works towards making the water effluent-free. Using an Effluent treatment plant, we convert wastewater - which is water no longer needed or suitable for its most recent use - into an effluent that can be either returned to the water cycle with minimal environmental issues or reused.
If an industry has a right to use water then it becomes their duty to make it clean or re-usable. Industries consumed clean water and in outcome they generate polluted water which includes harmful chemicals such as oils, grease, solids etc. water produced through the industrial process is called effluent. Our duty is to clean the pollutants through the effective water treatment methods. So, plants are established for this process and these plants are called "Effluent Treatment plants". As the name suggest, it involves removing the pollutants under the water to make it usable for another process and then to make the environment pollution free.
Combined Effluent Treatment Plants ( C-ETP )
CETP's are set up in the industrial estates where there are clusters of small scale industrial units and where many polluting industries are located. Many of the Small Scale Industries (SSI) are unable to install the individual treatment systems. Hence, the concept of CETP's (Common Effluent Treatment Plants) is envisaged to benefit such industries in treating its effluent before disposal whether it is in stream, land, sewerage system or in rivers and seas. The Ministry of Environment & Forest, Government of India has launched a centrally sponsored scheme, namely, Common Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP) in order to make a co-operative movement of pollution control especially to treat the effluent, emanating from group of compatible Small-Scale Industries. The CETP therefore, reduces the treatment cost to be borne by an individual member unit while protecting the water environment to a maximum.
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF)
Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) is a highly effective wastewater treatment process that removes suspended solids, oils, greases, and other contaminants. It's widely used in industries such as oil and gas, food processing, and manufacturing.
How DAF Works
- Air Injection: Air is compressed and injected into a portion of the wastewater, creating a saturated solution.
- Pressure Release: The pressurized wastewater is released into a flotation tank, where the pressure drops. This causes the dissolved air to form tiny bubbles.
- Flotation: The bubbles attach to suspended solids and other contaminants, causing them to float to the surface.
- Skimming: A skimming device removes the floating solids from the water surface, leaving clarified water.
Benefits of DAF
- High efficiency: Effectively removes suspended solids, oils, and greases.
- Versatile: Applicable to various wastewater types and industries.
- Compact design: Requires less space compared to other treatment methods.
- Low sludge production: Reduces sludge handling and disposal costs.
- Improved water quality: Produces high-quality effluent suitable for reuse or discharge.
Rain Water Treatment Plant
Rainwater Treatment Plants are essential components of rainwater harvesting systems, ensuring that collected rainwater is safe for its intended use. While rainwater is generally considered clean, it can contain pollutants like dust, debris, bird droppings, and even chemicals from rooftops. Therefore, treatment is crucial to remove contaminants and make the water suitable for various applications.
Applications of Treated Rainwater
Treated rainwater can be used for various purposes:
- Domestic use: Flushing toilets, laundry, gardening, and car washing.
- Agricultural irrigation: Supplying water to crops, reducing reliance on groundwater.
- Industrial processes: Cooling systems, cleaning equipment, and non-potable water requirements.
- Groundwater recharge: Replenishing aquifers and maintaining water table levels.
Benefits of Rainwater Treatment Plants
- Water conservation: Reduces dependence on municipal water supplies.
- Cost savings: Lower water bills and reduced wastewater treatment costs.
- Environmental protection: Reduces stormwater runoff and protects water bodies.
- Improved water quality: Provides a reliable source of clean water.

